A hotter planet, much less nutritious crops and … fewer grasshoppers?
[ad_1]
It’s robust on the market for a hungry grasshopper on the Kansas prairie. Oh, there’s loads of grass to eat, however this century’s grass isn’t what it was once. It’s much less nutritious, poor in minerals like iron, potassium and calcium.
Partly as a result of that nutrient-deficient weight loss program, there’s been a large decline in grasshopper numbers of late, by about one-third over twenty years, in accordance with a 2020 examine. The prairie’s not hoppin’ prefer it used to — and a serious wrongdoer is carbon dioxide, says examine writer Michael Kaspari, an ecologist on the College of Oklahoma in Norman.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide is at its highest in human historical past. That’s in all probability advantageous for crops just like the grasses the hoppers munch. They’ll flip that atmospheric carbon into carbohydrates and construct extra crops—in actual fact, plant biologists as soon as thought all that additional carbon dioxide would merely imply higher crop yields. However experiments in crops uncovered to excessive carbon dioxide ranges point out that many meals crops comprise much less of different vitamins than beneath carbon dioxide concentrations of the previous. A number of research discover that crops’ ranges of nitrogen, for instance, have fallen, indicating decrease plant protein content material. And a few research recommend that crops might also be poor in phosphorus and different hint parts.
The concept that crops grown in at this time’s carbon dioxide-rich period will comprise much less of sure different parts—an idea Kaspari categorizes as nutrient dilution—has been well-studied in crop crops. Nutrient dilution in pure ecosystems is less-studied, however scientists have noticed it occurring in a number of locations, from the woods of Europe to the kelp forests off Southern California. Now researchers like Kaspari are beginning to study the knock-on results—to see whether or not herbivores that eat these crops, comparable to grasshoppers and grazing mammals, are affected.
The scant information already current recommend nutrient dilution may trigger widespread issues. “I feel we’re in canary-in-a-coal mine territory,” Kaspari says.
Decrease-quality meals?
It’s clear that rising carbon dioxide ranges change plant make-up in quite a lot of methods. Scientists have carried out years-long research wherein they pump carbon dioxide over crops to artificially elevate their publicity to the fuel, then take a look at the crops for nutrient content material. One massive evaluation discovered that elevating carbon dioxide by about 200 elements per million boosted plant mass by about 18 %, however usually lowered ranges of nitrogen, protein, zinc and iron.
Greens like lettuce and tomatoes could also be sweeter and tastier as a result of added carbon-rich sugars, however lose out on some 10 % to twenty % of the protein, nitrate, magnesium, iron and zinc that they’ve in lower-carbon circumstances, in accordance with one other massive examine. On common, crops might lose about 8 % of their mineral content material in circumstances of elevated carbon dioxide. Kaspari likens the impact to buying and selling a nourishing kale salad for a bowl of low-nutrient iceberg lettuce.
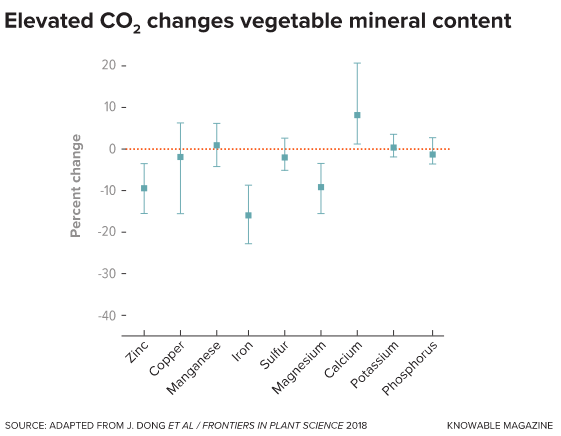
When greens are grown beneath elevated ranges of carbon dioxide, they usually get greater and sweeter and will have extra of some minerals, comparable to calcium, an evaluation of a number of completely different research discovered. However portions of different minerals, together with zinc and iron, can go down.
Scientists don’t but know precisely how additional carbon dioxide results in adjustments in all these different vitamins. Kaspari, who mentioned the significance of micronutrients comparable to calcium and iron in ecosystems within the 2021 Annual Overview of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, suggests it’s a easy problem of ratios: Carbon goes up however the whole lot else stays the identical.
Lewis Ziska, a plant physiologist on the Columbia College Mailman Faculty of Public Well being in New York Metropolis, thinks it’s extra sophisticated than simply ratios. For instance, within the vegetable examine, elevated carbon dioxide elevated the focus of sure vitamins, comparable to calcium, even because it restricted ranges of others.
One contributing issue may very well be crops’ little openings, referred to as stomata, by which they take up the carbon dioxide they use to make sugars and the remainder of their buildings. If there’s loads of carbon dioxide round, they don’t must open the stomata as usually, or for as lengthy. Which means crops lose much less moisture by way of evaporation from these openings. The end result may very well be much less liquid transferring up the stem from the roots, and since that liquid carries parts comparable to metals from soil, much less of these hint parts would attain the stems and leaves.
Scientists have additionally posited that when carbon dioxide is excessive, crops are much less environment friendly at taking on minerals and different parts as a result of the foundation molecules that usually pull in these parts are performing at a decrease capability. There are in all probability a number of processes at play, says Ziska. “It’s not a one-size-fits-all mechanism.”
No matter is happening in these well-studied crops, the identical factor is presumably occurring in timber and weeds and different non-agricultural species, says Kaspari. “If it’s occurring to the human meals provide, it’s occurring to everyone else.”
A number of research recommend that Kaspari is correct. For instance, although farmers add nitrogen fertilizer to croplands and that nitrogen then washes into neighboring waterways or wildlands, nitrogen availability is on the decline in quite a lot of non-agricultural ecosystems. In a single evaluation, researchers examined nitrogen ranges in additional than 43,000 leaf samples, collected in numerous research between 1980 and 2017. Atmospheric carbon dioxide ranges rose by almost 20 % throughout that interval, and nitrogen concentrations within the leaves decreased by 9 %. Mineral concentrations are additionally affected: Scientists who studied timber in Europe between 1992 and 2009 noticed a drop in a number of, together with calcium, magnesium, and potassium, in at the least a few of their leaf samples.
Scientists may also study museum and herbaria samples to review how plant nutrient content material has modified as planetary carbon dioxide ranges have risen. Ziska and colleagues did so for goldenrod, a key meals supply for bees. Utilizing collections from the Smithsonian Establishment’s pure historical past museum in Washington, DC, they analyzed pollen from way back to 1842, simply earlier than the American Industrial Revolution. At the moment, the carbon dioxide ranges have been 280 elements per million, in comparison with simply over 420 at this time.
Pollen protein content material, and thus diet stage, decreased over time by about one-third, the scientists discovered. Ziska’s fashionable experiments with goldenrod grown beneath carbon dioxide ranges as excessive as 500 elements per million confirmed that extra carbon dioxide yields protein-deficient pollen. Although it’s not clear but what this implies for bees, it’s in all probability not good, Ziska says.
The outcomes are putting, notably in contrast with crop research that don’t draw on massive historic datasets, says Samuel Myers, a principal analysis scientist on the Harvard T.H. Chan Faculty of Public Well being who has investigated the hyperlink between the well being of pollinators and human diet.
[ad_2]
No Comment! Be the first one.